Different Properties Of Vertically Aligned Carbon Nanotubes Used In Labs
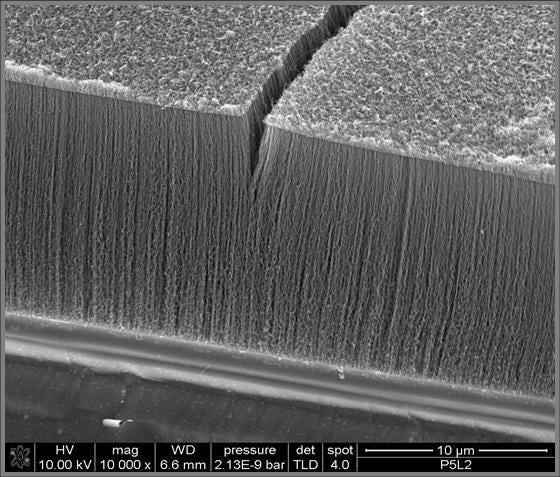
A carbon nanotube is a popular material among scientists working in the field of nanotechnology. These nanotubes may be created in a vertical or horizontal position, as needed by the scientists. The properties of these thin sheets of single-layered carbon molecules rolled into cylinders somewhat differ based on their original manufacturing positions. The experiments done with these nanoparticles depend on their specific physical and chemical properties.
Prime features of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes
Since the vertical carbon nanotubes are amorphous and macroporous, they easily react with all metals and get fixed to any metal plate speedily. This binding capability has made the vertically aligned carbon nanotubes to be the first choice of scientists for several relevant applications.
These vertical carbon nanotubes are optically very sensitive, making them the ideal choice in applying for many optical experiments. Due to the rough surface of these nanotubes, their refractive index is quite low and thus, they have the capacity of absorbing large amounts of light.
The carbon nanotubes are both thermally and electrically superconductive, for which these vertical nanoparticles are more preferred in making parts of electrical appliances. The greater electrochemical stability of these nanotubes helps in faster reactions when used for making supercapacitors to be installed in many devices.
Notable scientific uses of vertically arranged carbon nanotubes
Due to the presence of unique optical properties, these vertically arranged carbon nanotubes are used in manufacturing visual devices, like telescopes, spectroscopes, and microscopes. Sensory tools used for detecting some harmful gases in the surrounding air are also made of these sensitive nanotubes. Similarly, such detectors are also needed for finding many biological matters in the laboratories. These nanoparticles are also used successfully as catalysts in chemical experiments, as carbon remains inactive with many other chemicals. Tiny transistors and batteries are also made with these conductive nanotubes.
Hence, the vertical carbon nanotubes are produced and purchased in bulk amounts by scientists of various streams.